Contents
- I. Introduction to Athlete’s Guide to Nutrition
- II. Importance of Proper Nutrition for Athletes
- III. Key Macronutrients for Athletes
- IV. Micronutrients and their Role in Athletic Performance
- V. Meal Planning Tips for Athletes
- VI. Pre- and Post-Workout Nutrition for Optimal Performance
- VII. Hydration and its Impact on Athletic Performance
- VIII. Common Myths and Misconceptions about Athlete Nutrition
- 1. Myth: Athletes should only focus on protein intake
- 2. Myth: Supplements can replace a balanced diet
- 3. Myth: More calories always mean better performance
- 4. Myth: Avoiding carbohydrates leads to weight loss
- 5. Myth: Hydration isn’t crucial during indoor workouts or colder weather
- 6. Myth: Fat should be completely avoided
- 7. Myth: Skipping meals can help with weight loss
- 8. Myth: All athletes require the same nutrition plan
- IX. Frequently Asked Questions about Athlete’s Nutrition
- 1. What is the importance of nutrition for athletes?
- 2. How many calories should athletes consume?
- 3. What macronutrients are essential for athletes?
- 4. Should athletes follow a specific diet plan?
- 5. Is it necessary to take supplements as an athlete?
- 6. How does hydration impact athletic performance?
- 7. Are there any specific foods that athletes should avoid?
- 8. Should athletes eat before and after workouts?
- 9. Can nutrition aid in injury prevention?
- 10. How can athletes ensure they are meeting their nutritional needs?
I. Introduction to Athlete’s Guide to Nutrition

As an athlete, your performance is directly influenced by the fuel you provide your body. Proper nutrition plays a vital role in optimizing athletic performance, enhancing recovery, and supporting overall health. The Athlete’s Guide to Nutrition aims to provide you with valuable insights and practical tips on how to fuel your body effectively.
1. Importance of Proper Nutrition for Athletes
Nutrition is the cornerstone of athletic success. It affects every aspect of your performance, from energy levels and endurance to strength and recovery. By consuming a balanced diet that meets your specific needs as an athlete, you can enhance your training results and achieve peak performance.
2. Macronutrients: The Building Blocks of Performance
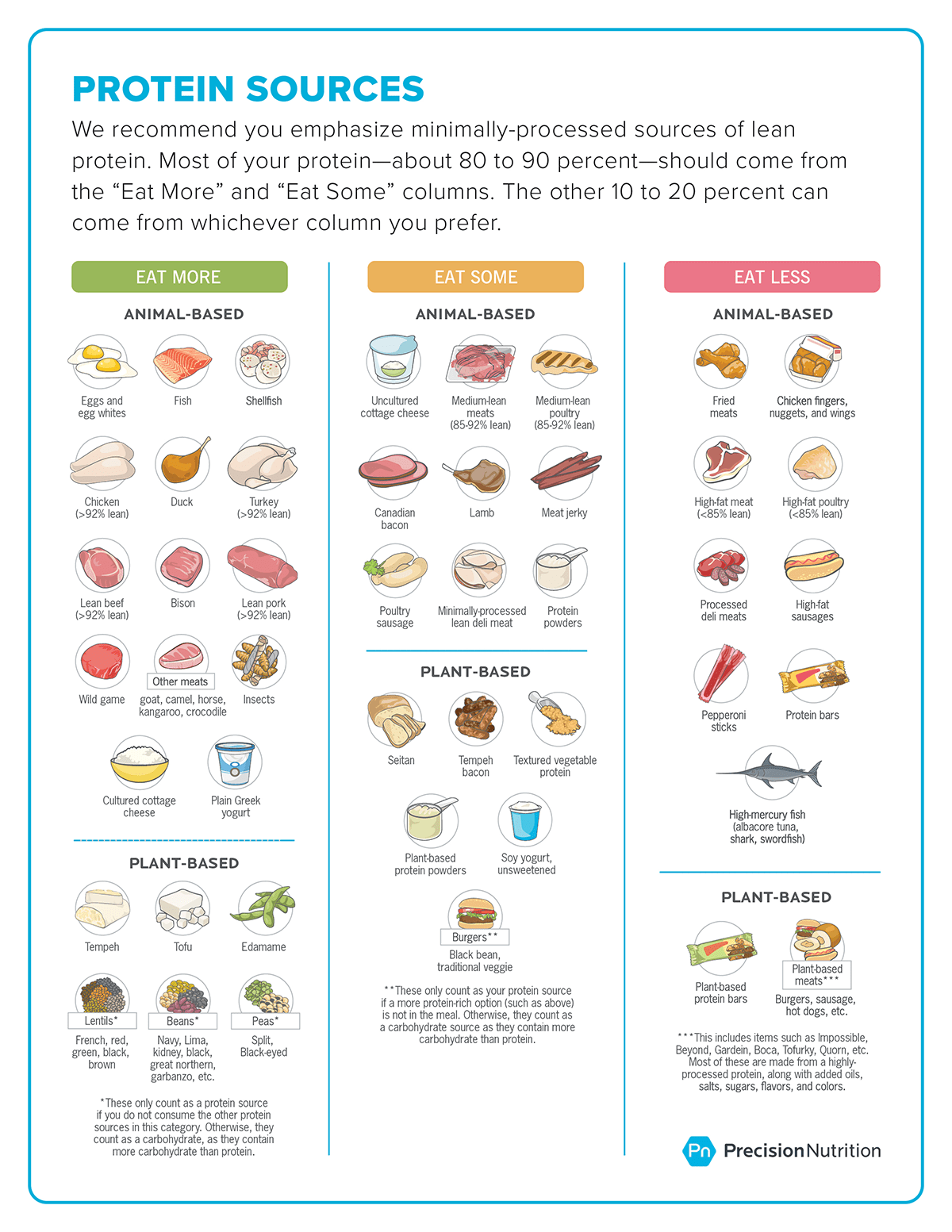
The three macronutrients – carbohydrates, proteins, and fats – are essential for athletes as they provide the energy needed for physical activity and support muscle growth and repair. Understanding how these macronutrients function in the body will help you optimize their intake for maximum athletic benefit.
3. Micronutrients: The Powerhouse Supporters
In addition to macronutrients, micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals play a crucial role in maintaining optimal health and supporting various bodily functions involved in athletic performance. Discover which micronutrients are particularly important for athletes and how you can ensure their adequate intake through proper food choices.
4. Hydration: Staying Atop Your Game
Adequate hydration is key for athletes as even mild dehydration can impair physical performance significantly. Learn about the importance of hydration before, during, and after exercise sessions or competitions along with strategies to maintain proper fluid balance throughout the day.
5. Pre-Workout and Post-Workout Nutrition
The timing and composition of your meals before and after training sessions are crucial for maximizing performance gains, enhancing recovery, and promoting muscle growth. Explore the optimal pre-workout and post-workout nutrition strategies to fuel your workouts effectively.
6. Sports Supplements: Understanding the Options
Supplements can be a useful addition to an athlete’s nutrition plan when used properly. Get insights into various sports supplements commonly used by athletes, their potential benefits, safety considerations, and guidance on making informed decisions regarding supplementation.
The Athlete’s Guide to Nutrition is designed to empower you with knowledge that will enable you to make informed choices about the food you consume as an athlete. By optimizing your nutritional intake in alignment with your training goals, you can unlock your full athletic potential while ensuring long-term health and well-being.
II. Importance of Proper Nutrition for Athletes

Athletes require a well-balanced and nutritious diet to fuel their bodies for optimal performance. The importance of proper nutrition cannot be overstated when it comes to achieving peak physical fitness and reaching athletic goals.
1. Enhanced Performance
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in enhancing an athlete’s performance. By consuming the right balance of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), athletes can optimize their energy levels, improve endurance, speed up recovery, and increase strength. Nutrient-dense foods provide the necessary fuel for muscles during training sessions or competitions.
2. Injury Prevention
Adequate nutrition is crucial for preventing injuries among athletes. Consuming nutrient-rich foods helps build strong bones, maintain healthy joints, strengthen connective tissues, and boost the immune system—essential components in reducing the risk of injuries such as fractures or sprains.
3. Muscle Growth and Repair
Nutrition plays a significant role in muscle growth and repair processes after intense workouts or competitions. Protein-rich foods aid in muscle recovery by repairing damaged tissues caused by exercise-induced stressors like weightlifting or high-intensity training sessions.
4. Optimal Body Composition
Maintaining an optimal body composition is essential for athletes to maximize their performance potential. A well-rounded diet consisting of lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, healthy fats, fruits, vegetables ensures that athletes achieve an ideal balance between muscle mass and body fat percentage that suits their specific sport requirements.
5.Replenishing Electrolytes
Sweating during physical activity leads to electrolyte loss from the body which can result in dehydration and hinder performance. Athletes must replenish electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium through proper nutrition. Including foods like bananas, nuts, whole grains, or sports drinks can help maintain electrolyte balance.
6. Mental Focus and Cognitive Function
Proper nutrition not only benefits athletes physically but also mentally. Consuming a diet rich in vitamins, minerals, omega-3 fatty acids promotes brain health and enhances cognitive function. This is crucial for maintaining mental focus during training sessions or competitions.
7. Overall Health and Well-being
Athletes are prone to pushing their bodies to the limit regularly; therefore, it is paramount to prioritize overall health and well-being through proper nutrition. A balanced diet helps reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease or diabetes while promoting longevity.
By understanding the importance of proper nutrition for athletes, individuals can make informed choices regarding their dietary habits to optimize performance levels on and off the field.
III. Key Macronutrients for Athletes
Athletes require a well-balanced diet that provides the necessary macronutrients to support their training, performance, and recovery. These macronutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Let’s explore each of these essential nutrients in detail:
1. Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for athletes as they provide glucose, which fuels our muscles and brain. Consuming an adequate amount of carbohydrates is crucial for optimal athletic performance.
Athletes should focus on consuming complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes rather than simple sugars found in processed foods. Complex carbs provide sustained energy release while simple sugars can lead to rapid energy spikes followed by crashes.
2. Proteins
Proteins play a vital role in muscle repair and growth after intense exercise or training sessions. Athletes need higher protein intake compared to sedentary individuals to support muscle recovery and promote lean muscle mass development.
Incorporate lean sources of protein such as chicken breast, fish, tofu, beans, Greek yogurt into your diet. It’s important to spread out protein intake throughout the day to optimize absorption and utilization by the body.
3. Fats
Fats are often misunderstood but are an essential component of a healthy diet for athletes too. They provide a concentrated source of energy during prolonged endurance activities while also supporting hormone production and nutrient absorption.
Avoid trans fats found in fried foods or processed snacks as they can negatively impact health outcomes. Instead, focus on consuming unsaturated fats like avocados, nuts/seeds,
and olive oil that have numerous cardiovascular benefits.
4. Hydration
While not a macronutrient, hydration is crucial for athletes. Staying properly hydrated optimizes performance and aids in recovery. Aim to drink enough water throughout the day and increase your intake during intense workouts or hot weather conditions.
It’s important to remember that every athlete has unique nutritional needs based on their sport, training intensity, body composition goals, and individual preferences. Consulting with a registered dietitian who specializes in sports nutrition can help tailor a nutrition plan specific to your needs.
5. Supplementation
In some cases, athletes may benefit from supplements to fill nutrient gaps or enhance performance. However, it’s essential to approach supplementation cautiously and consult with healthcare professionals before adding any new products to your routine.
If considering supplements like protein powders or vitamins/minerals, ensure they are from reputable brands that undergo third-party testing for quality assurance.
Remember, maintaining a balanced diet that includes adequate macronutrients is key for optimizing athletic performance and supporting overall health and well-being.
IV. Micronutrients and their Role in Athletic Performance
Micronutrients are essential nutrients that the body needs in small amounts to function properly. While macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats provide the energy necessary for physical activity, micronutrients play a crucial role in supporting overall health and optimizing athletic performance.
1. Vitamin C: Enhancing Immune Function
Vitamin C is known for its immune-boosting properties due to its antioxidant effects. For athletes, maintaining a strong immune system is vital as intense training can temporarily suppress immunity. Including vitamin C-rich foods such as citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers can help reduce the risk of illness or infections that may hinder performance.
2. Iron: Oxygen Transport and Energy Production
Iron plays a key role in transporting oxygen throughout the body via red blood cells. During exercise, iron helps deliver oxygen to working muscles efficiently, promoting endurance and preventing fatigue. Include iron-rich foods like lean meats, spinach, lentils, and fortified cereals to ensure an adequate supply of this essential mineral.
3. B Vitamins: Energy Metabolism
The B vitamins consist of several important nutrients such as thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), pyridoxine (B6), biotin (B7), folate (B9), and cobalamin (B12). These vitamins play a crucial role in converting food into energy by aiding in carbohydrate metabolism. Ensuring sufficient intake of B vitamins through sources like whole grains, poultry, fish, eggs, nuts can support optimal energy production for athletic performance.
4. Calcium: Bone Health and Muscle Function
Calcium is well-known for its role in maintaining strong bones, but it also plays a significant role in muscle function. During exercise, calcium helps muscles contract and relax effectively. Consuming calcium-rich foods like dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based milk alternatives can support bone health and muscular performance.
5. Vitamins A and E: Antioxidant Protection
Vitamins A and E are powerful antioxidants that help protect the body against oxidative stress caused by intense physical activity. These vitamins neutralize free radicals generated during exercise, reducing inflammation and promoting recovery. Including foods like carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach (vitamin A), nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils (vitamin E) can help athletes combat the negative effects of oxidative stress.
Incorporating a well-balanced diet rich in these essential micronutrients can have a profound impact on an athlete’s overall health and performance potential. However, individual needs may vary depending on factors such as age, sex, training intensity/duration or specific dietary restrictions.
Remember to consult with a qualified sports nutritionist or healthcare professional to ensure personalized recommendations tailored to your specific requirements as an athlete.
V. Meal Planning Tips for Athletes
Proper nutrition is essential for athletes to support their performance, recovery, and overall health. Meal planning plays a crucial role in ensuring that athletes meet their nutritional needs and optimize their athletic potential. Here are some valuable meal planning tips specifically designed for athletes:
1. Prioritize Balanced Macronutrient Intake
Athletes should focus on consuming a balanced mix of macronutrients – carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats – in every meal. Carbohydrates provide energy for workouts, proteins aid muscle repair and growth, while healthy fats support hormone production and reduce inflammation.
2. Time Your Meals Around Workouts
The timing of your meals can significantly impact your athletic performance. Consume a carbohydrate-rich meal or snack 1-4 hours before exercise to fuel your muscles adequately. Additionally, aim to consume protein within 30 minutes after completing a workout to promote muscle recovery.
3. Emphasize Whole Foods
Incorporate whole foods into your meals as much as possible instead of relying on processed foods or supplements alone. Whole foods offer a wide range of nutrients that promote better overall health and provide the necessary micronutrients required by athletes.
4. Stay Hydrated
Adequate hydration is crucial for optimal athletic performance and recovery. Make sure you drink enough water throughout the day to maintain proper hydration levels during training sessions or competitions.
5 Maintain Consistency with Eating Habits
Eating at regular intervals helps stabilize blood sugar levels and provides sustained energy throughout the day for training or competing events.
6 Listen To Your Body’s Hunger Cues
Paying attention to your body’s hunger and fullness signals is essential for maintaining a healthy relationship with food. Eat when you’re hungry, and stop eating when you’re satisfied, rather than using external cues.
7. Plan Your Meals in Advance
Planning your meals ahead of time can help ensure that you have nutritious options readily available. This practice also allows you to make healthier choices and avoid resorting to convenient but less nutritious options when hunger strikes.
8. Seek Professional Guidance
If you want personalized meal planning advice tailored specifically to your athletic goals, consider consulting a registered dietitian or nutritionist who specializes in sports nutrition.
By following these meal planning tips, athletes can fuel their bodies effectively, enhance performance, support recovery, and maintain overall health and well-being.
VI. Pre- and Post-Workout Nutrition for Optimal Performance
When it comes to athletic performance, proper nutrition plays a crucial role in maximizing results. Both pre- and post-workout meals are essential for fueling your body, optimizing energy levels, and promoting muscle recovery. Let’s dive into the key considerations for pre- and post-workout nutrition to help you achieve optimal performance.
1. Pre-Workout Fuel: Energize Your Body
Prior to engaging in any physical activity, it’s important to provide your body with the right fuel. Aim for a balanced meal that includes carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats about 1-2 hours before your workout session. Carbohydrates will provide the necessary energy while protein aids in muscle repair.
You can opt for whole grain toast with peanut butter and banana or Greek yogurt topped with berries and nuts as excellent pre-workout options. These choices offer a good mix of macronutrients that will sustain you during exercise.
2. Hydration: A Crucial Aspect
Maintaining proper hydration is vital before, during, and after workouts to prevent dehydration which can negatively impact performance levels. Drink water regularly throughout the day leading up to your workout session.
Avoid sugary drinks or excessive caffeine intake as they may cause dehydration due to their diuretic effects on the body.
3. Post-Workout Recovery: Repairing Muscles
The period following exercise is crucial for muscle repair and replenishing glycogen stores used during physical activity.
Incorporate both carbohydrates and protein into your post-workout meal within 30 minutes of completing your workout session. This combination helps restore glycogen levels while promoting muscle protein synthesis.
Opt for a protein shake with added fruits or a chicken breast with sweet potato and vegetables as your post-workout meal. These options provide the necessary nutrients to aid in recovery and optimize performance for your next session.
4. Timing is Key
The timing of your pre- and post-workout meals is crucial in maximizing their benefits. Aim to consume your pre-workout meal 1-2 hours before exercising, allowing sufficient time for digestion.
Post-workout nutrition should be consumed within the first 30 minutes after exercise when muscle cells are most receptive to nutrient absorption.
VII. Hydration and its Impact on Athletic Performance
Hydration plays a crucial role in optimizing athletic performance. As an athlete, it is essential to understand how proper hydration affects your body’s ability to perform at its peak. This section will delve into the importance of hydration and provide valuable insights on how to maintain optimal hydration levels for enhanced athletic performance.
The Significance of Hydration
Staying adequately hydrated is vital for athletes as it directly impacts their physical and mental capabilities during training sessions and competitions. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, muscle cramps, decreased cognitive function, and impaired decision-making abilities. By maintaining proper hydration levels, athletes can avoid these detrimental effects and perform at their best.
Optimal Fluid Intake
Athletes should aim to consume fluids regularly throughout the day rather than relying solely on drinking during workouts or competitions. The recommended daily fluid intake varies based on factors such as body weight, activity level, temperature, humidity, and sweat rate. It is advisable to consult with a sports nutritionist or healthcare professional who can determine your individual fluid requirements.
Pre-Workout Hydration Strategies
Prioritizing pre-workout hydration is essential for maximizing performance. Drinking sufficient fluids before exercise helps ensure that you start your training session or competition in a properly hydrated state. Aim to consume around 500-600 milliliters (16-20 ounces) of water or a sports drink 2-4 hours before physical activity.
During Exercise Hydration Techniques
To maintain adequate fluid balance during exercise, it’s important to drink fluids at regular intervals. The American College of Sports Medicine recommends consuming approximately 200-300 milliliters (7-10 ounces) of fluid every 10-20 minutes during exercise. This guideline can vary depending on factors such as intensity, duration, and environmental conditions. It’s crucial to listen to your body’s thirst cues and drink accordingly.
Post-Workout Rehydration
Replenishing fluids after exercise is essential for recovery. Aim to consume 1.5 times the weight lost during the workout within two hours post-exercise. For example, if you lost 1 kilogram (2.2 pounds) during a training session, consume around 1.5 liters (50 ounces) of fluid to restore hydration levels effectively.
In addition to fluids, incorporating electrolytes into your post-workout rehydration strategy can be beneficial, especially if you engaged in prolonged or intense exercise that resulted in significant sweat loss.
Remember that individual hydration needs may vary based on factors like sweat rate, climate conditions, and personal differences. Monitoring urine color is an easy way to assess hydration status: pale yellow indicates proper hydration while dark yellow suggests dehydration.
By understanding the significance of proper hydration and implementing strategies tailored to your specific needs as an athlete, you can optimize your performance potential and maintain overall well-being throughout your athletic journey.
VIII. Common Myths and Misconceptions about Athlete Nutrition
Athlete nutrition is a widely discussed topic, but unfortunately, there are many myths and misconceptions surrounding it. Let’s debunk some of the most common ones:
1. Myth: Athletes should only focus on protein intake
While protein is essential for muscle repair and growth, a well-rounded diet is crucial for overall performance. Carbohydrates provide energy, fats support hormone production, vitamins and minerals aid in various bodily functions – all of which are necessary for athletes to excel.
2. Myth: Supplements can replace a balanced diet
Supplements can be beneficial in certain cases, but they should never replace whole foods. A varied diet consisting of lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats provides the necessary nutrients that supplements cannot replicate.
3. Myth: More calories always mean better performance
Eating excessive calories without considering their quality can hinder rather than enhance athletic performance. It’s important to focus on nutrient-dense foods that provide sustained energy throughout workouts rather than relying solely on high-calorie options.
4. Myth: Avoiding carbohydrates leads to weight loss
Carbohydrates are often misunderstood as being detrimental to weight management; however, they are an essential source of fuel for athletes’ bodies during intense physical activity. The key is to choose complex carbs like whole grains instead of refined sugars or processed foods.
5. Myth: Hydration isn’t crucial during indoor workouts or colder weather
Sweating may not be as noticeable during indoor exercises or in colder climates; however dehydration can still occur due to increased breathing rate and water loss through respiration even when we don’t feel hot or sweaty. Staying adequately hydrated is vital for optimal performance and recovery.
6. Myth: Fat should be completely avoided
Fat is often unfairly associated with weight gain, but it’s a necessary macronutrient that provides energy and aids in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Choosing healthy fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil can support overall health without compromising athletic performance.
7. Myth: Skipping meals can help with weight loss
Skipping meals may seem like an easy way to cut calories; however, it can negatively impact an athlete’s energy levels and lead to poor recovery. Eating regular balanced meals throughout the day helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and supports sustained energy for workouts.
8. Myth: All athletes require the same nutrition plan
Every athlete has unique nutritional needs based on their sport, body composition goals, training intensity, and individual preferences. It’s essential to work with a qualified sports nutritionist or registered dietitian who can create a personalized plan tailored to specific requirements.
IX. Frequently Asked Questions about Athlete’s Nutrition
Here are some common questions athletes often have about nutrition:
1. What is the importance of nutrition for athletes?
Nutrition plays a vital role in an athlete’s performance and overall health. It provides the necessary fuel for energy, aids in recovery, enhances strength and endurance, and supports optimal body composition.
2. How many calories should athletes consume?
The calorie needs of athletes vary depending on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and goals. It is important to consult with a sports dietitian or nutritionist to determine individual caloric requirements based on specific needs.
3. What macronutrients are essential for athletes?
Athletes require adequate amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to meet their nutritional needs. Carbohydrates provide energy for exercise, proteins aid in muscle repair and growth, while fats help with hormone production and nutrient absorption.
4. Should athletes follow a specific diet plan?
An athlete’s dietary plan should be tailored to their individual needs and goals. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, focusing on whole foods rich in nutrients is generally recommended along with proper hydration.
5. Is it necessary to take supplements as an athlete?
In most cases, getting nutrients from whole foods is preferable over relying solely on supplements; however certain situations may warrant supplementation under the guidance of a healthcare professional or sports dietitian.
6. How does hydration impact athletic performance?
Maintaining proper hydration levels is crucial for optimal athletic performance as even slight dehydration can negatively affect physical abilities such as endurance and cognitive function.
7. Are there any specific foods that athletes should avoid?
Avoiding highly processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated fats is generally recommended. These types of foods can hinder performance and negatively impact overall health.
8. Should athletes eat before and after workouts?
Eating a balanced meal or snack before exercise provides the necessary fuel for optimal performance, while consuming a combination of carbohydrates and proteins within the post-workout window aids in muscle recovery.
9. Can nutrition aid in injury prevention?
Nutrition plays a role in supporting strong bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments which are essential for injury prevention. Consuming adequate amounts of vitamins, minerals, and protein can contribute to overall musculoskeletal health.
10. How can athletes ensure they are meeting their nutritional needs?
Maintaining a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods is key to meeting an athlete’s nutritional needs. Regular monitoring by professionals such as sports dietitians can provide personalized guidance based on individual goals and requirements.

Shelby Cortez is a dynamic and passionate individual with a strong background in the fitness industry. With a Bachelor’s degree in Exercise Science from the prestigious University of California, she has gained extensive knowledge about the human body and its mechanics. Shelby’s dedication to fitness goes beyond her education, as she has spent years honing her skills as a personal trainer and group fitness instructor. Her expertise in workout routines and nutrition has helped countless individuals achieve their fitness goals. Shelby’s commitment to health and wellness is evident in her own lifestyle, as she consistently pushes herself to new limits in the gym. Whether it’s weightlifting, yoga, or HIIT workouts, Shelby Cortez is the go-to expert for all things fitness-related.

