Contents
- I. Introduction to Recovery Nutrition Principles
- II. Understanding the Importance of Recovery Nutrition
- III. Key Nutrients for Optimal Recovery
- IV. Timing and Frequency of Post-Workout Nutrition
- V. Tailoring Recovery Nutrition to Individual Needs
- VI. Common Mistakes to Avoid in Recovery Nutrition
- VII. Frequently Asked Questions about Recovery Nutrition Principles
- 1. What is recovery nutrition?
- 2. Why is recovery nutrition important?
- 3. What are the key components of a post-workout meal?
- 4. How soon after exercise should I consume my post-workout meal?
- 5. Can I rely on supplements alone for recovery nutrition?
- 6. Do I need to adjust my recovery nutrition based on the type of exercise?
- 7. Can I have a cheat meal after a workout?
- 8. How much water should I drink during my recovery period?
- 9. Is it necessary to track macros and calories for post-workout meals?
- 10. Are there any special considerations for vegetarian or vegan athletes regarding recovery nutrition?
I. Introduction to Recovery Nutrition Principles

When it comes to optimizing your recovery after intense physical activity, nutrition plays a vital role in replenishing energy stores and repairing muscle damage. Recovery nutrition principles focus on providing the necessary nutrients that aid in the body’s repair and regeneration processes, allowing you to bounce back stronger and faster.
The Importance of Post-Workout Nutrition
After an intense workout or competition, your body is in a state of depleted glycogen stores and micro-tears in muscle fibers. This is where post-workout nutrition becomes crucial. Consuming the right nutrients within the optimal timeframe helps kickstart the recovery process by replenishing glycogen levels, promoting protein synthesis, reducing inflammation, and enhancing overall recovery.
The Role of Protein
Protein is an essential macronutrient for muscle repair and growth. Including high-quality protein sources such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products or plant-based alternatives like beans or tofu can provide your body with the necessary amino acids it needs for optimal recovery. Aim for around 20-30 grams of protein within 30 minutes to an hour after exercise to maximize muscle protein synthesis.
The Significance of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are essential for replenishing glycogen stores in muscles and liver after strenuous exercise. Opt for complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, vegetables instead of simple sugars that can cause blood sugar spikes followed by crashes. Consuming carbohydrates alongside protein post-workout enhances glycogen repletion while supporting muscle repair.
The Power of Antioxidants
Athletes often experience increased oxidative stress during intense physical activities due to free radicals produced by metabolism. Antioxidants found in colorful fruits and vegetables help combat this stress and reduce inflammation. Including a variety of antioxidant-rich foods such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts can aid in the recovery process and support overall health.
The Role of Hydration
Hydration is paramount for optimal recovery. During exercise, you lose significant amounts of fluid through sweat, which can lead to dehydration if not replenished. Adequate hydration helps transport nutrients to cells, aids in muscle repair, and regulates body temperature. Ensure you drink enough water before, during, and after workouts or competitions to maintain proper hydration levels.
By understanding the principles of recovery nutrition and implementing them into your post-workout routine, you can enhance your body’s ability to recover effectively. Remember to tailor your nutrition plan according to individual needs and goals while consulting with a qualified professional for personalized guidance.
II. Understanding the Importance of Recovery Nutrition
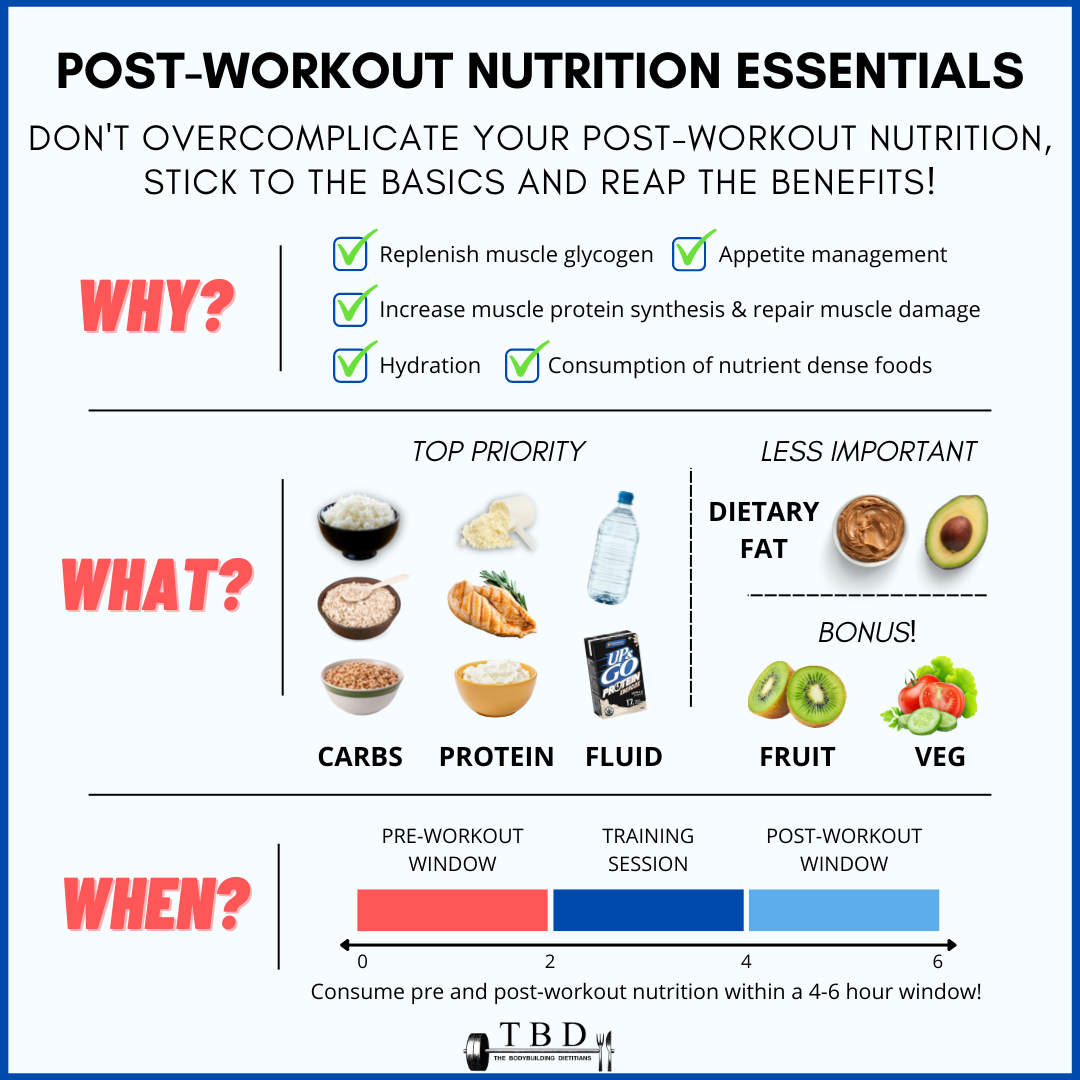
When it comes to athletic performance and overall fitness, recovery nutrition plays a crucial role in optimizing results. After intense exercise or training sessions, the body needs proper nourishment to repair and rebuild muscles, replenish energy stores, and promote overall recovery. Here are some key aspects to understand about the importance of recovery nutrition:
Fueling Muscles for Repair
Engaging in strenuous physical activities leads to muscle damage at a microscopic level. Consuming adequate protein after exercise provides essential amino acids that support muscle protein synthesis, aiding in their repair and growth. Including quality sources of protein such as lean meats, eggs, dairy products, or plant-based alternatives like tofu or legumes can contribute significantly to this process.
Replenishing Energy Stores
During exercise or intense physical activity, the body depletes its glycogen stores – the primary source of energy for muscles. Consuming carbohydrates following workouts helps restore these glycogen levels efficiently while providing immediate energy for post-workout recovery processes.
Aiding Hydration Levels
Sweating during workouts leads to fluid loss which can result in dehydration if not properly addressed. Rehydration is essential for optimal recovery as it helps regulate body temperature and supports nutrient transportation throughout the body. Combining fluids with electrolytes like sodium and potassium further aids in hydrating effectively.
Reducing Inflammation & Oxidative Stress
Vigorous exercise generates an inflammatory response within the body due to increased oxidative stress caused by free radicals production. Including antioxidant-rich foods such as berries, leafy greens, nuts, or seeds can help combat this inflammation while promoting faster recovery.
Promoting Restful Sleep
Adequate recovery nutrition also plays a significant role in promoting quality sleep. Certain nutrients, such as magnesium and tryptophan found in foods like bananas, almonds, or turkey, can enhance relaxation and improve sleep quality. Restful sleep is crucial for muscle repair and overall recovery.
Understanding the importance of recovery nutrition allows athletes and fitness enthusiasts to maximize their performance gains while minimizing the risk of injuries or burnout. By providing the necessary nutrients for optimal muscle repair, energy replenishment, hydration support, inflammation reduction, and promoting restful sleep; individuals can achieve faster recovery times and maintain consistent progress towards their fitness goals.
III. Key Nutrients for Optimal Recovery

When it comes to optimizing your recovery after intense physical activity, providing your body with the right nutrients is crucial. These key nutrients play a vital role in supporting muscle repair, reducing inflammation, replenishing energy stores, and enhancing overall recovery. Incorporating these nutrients into your post-workout meals and snacks can help you bounce back faster and perform better in subsequent training sessions.
The Importance of Protein
Protein is an essential nutrient for optimal recovery as it aids in muscle repair and growth. Consuming an adequate amount of protein after exercise can accelerate the healing process by repairing damaged muscle fibers.
To maximize the benefits of protein consumption, aim for a combination of high-quality animal or plant-based protein sources such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, tofu or tempeh. Including a source of protein in each post-workout meal will provide your body with the necessary building blocks to rebuild and recover.
Energizing Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are another crucial nutrient for recovery as they replenish glycogen stores that get depleted during exercise. Glycogen is the primary fuel source used by muscles during physical activity.
Incorporating complex carbohydrates like whole grains (such as brown rice or quinoa), fruits and vegetables into your post-workout meals will not only provide you with sustained energy but also aid in restoring glycogen levels quickly.
The Power of Antioxidants
Antioxidants play a significant role in reducing exercise-induced oxidative stress on the body caused by intense physical activity. Foods rich in antioxidants help combat free radicals that can damage cells and contribute to inflammation.
Include antioxidant-rich foods such as berries, dark leafy greens, citrus fruits, nuts, and seeds in your recovery meals to support the body’s natural defense system against oxidative stress.
Rehydrating with Fluids
Proper hydration is essential for optimal recovery. Fluids help transport nutrients to your muscles and facilitate the removal of waste products. Replenishing fluids lost through sweat during exercise is crucial for maintaining overall hydration status.
In addition to water, consider incorporating electrolyte-rich fluids like sports drinks or coconut water into your post-workout routine. These beverages can help restore electrolyte balance and replenish minerals lost during intense physical activity.
The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are healthy fats known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Including sources of omega-3 fatty acids such as fish (salmon, mackerel), walnuts, chia seeds or flaxseeds in your recovery meals can aid in reducing inflammation and supporting the healing process.
Consuming a balanced diet that includes these key nutrients will provide the necessary support for optimal recovery after intense physical activity. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized nutrition advice based on your individual needs and goals.
IV. Timing and Frequency of Post-Workout Nutrition

When it comes to optimizing your post-workout nutrition, timing and frequency play a crucial role in replenishing your body’s energy stores, promoting muscle recovery, and maximizing the benefits of your workout. Here are some key considerations for timing and frequency:
The 30-Minute Rule: Fueling Your Body Immediately After Exercise
Experts recommend consuming a balanced post-workout meal or snack within 30 minutes of completing your exercise session. This window of time is known as the “anabolic window,” during which your muscles are more receptive to nutrient absorption.
Your post-workout meal should ideally include a combination of carbohydrates and protein. Carbohydrates help restore glycogen levels, while proteins provide essential amino acids for muscle repair and growth. Consider options like a fruit smoothie with Greek yogurt or a turkey sandwich on whole grain bread.
Fueling Throughout the Day: Frequent Small Meals
In addition to the immediate post-workout meal, it is beneficial to eat small meals or snacks every few hours throughout the day. This approach helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, provides sustained energy, supports muscle repair, and prevents overeating at main meals.
Each mini-meal should contain a balance of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats) as well as micronutrients (vitamins and minerals). Opt for nutrient-dense foods such as lean meats or plant-based protein sources like beans or tofu paired with whole grains and vegetables.
Tailoring Nutrition Based on Exercise Intensity
The intensity level of your workout can influence how much you need to eat after exercising. High-intensity workouts deplete glycogen stores more rapidly than moderate-intensity activities. Therefore, if you engaged in a rigorous training session, it is important to prioritize carbohydrate intake to replenish glycogen stores effectively.
For moderate-intensity workouts such as brisk walking or cycling, a balanced mix of carbohydrates and protein is still essential for optimal recovery. Adjust your portion sizes accordingly based on the duration and intensity of your exercise.
Hydration: Essential for Optimal Recovery
In addition to post-workout nutrition, rehydrating your body is crucial after any physical activity. During exercise, you lose fluids through sweat, which need to be replenished. Aim to drink water or electrolyte-rich beverages within the first hour following your workout.
Remember that individual hydration needs may vary depending on factors like climate and personal sweat rate. Monitor your urine color as a general indicator of hydration status – pale yellow indicates adequate hydration.
V. Tailoring Recovery Nutrition to Individual Needs
When it comes to recovery nutrition, one size does not fit all. Each individual has unique needs and goals, and tailoring their nutrition plan accordingly can optimize the recovery process. Here are some key factors to consider when customizing recovery nutrition:
1. Macronutrient Ratios
The first step in tailoring recovery nutrition is determining the optimal macronutrient ratios for each individual. This involves assessing their energy expenditure, body composition goals, and activity level.
For endurance athletes, a higher proportion of carbohydrates may be necessary to replenish glycogen stores depleted during prolonged exercise. Strength athletes, on the other hand, may benefit from a higher protein intake to support muscle repair and growth.
2. Timing of Nutrient Intake
The timing of nutrient intake plays a crucial role in optimizing recovery. Consuming a combination of carbohydrates and protein within 30 minutes after exercise can enhance muscle glycogen replenishment and promote muscle protein synthesis.
Additionally, spacing out meals throughout the day ensures a steady supply of nutrients for ongoing repair processes.
3. Hydration Strategies
Adequate hydration is essential for efficient recovery post-exercise. The amount of fluid required varies depending on factors such as sweat rate and environmental conditions.
Incorporating electrolytes into hydration strategies can help replace lost minerals and maintain fluid balance more effectively.
4. Micronutrient Considerations
In addition to macronutrients, it’s important not to overlook micronutrients when tailoring recovery nutrition plans.
Certain vitamins (such as vitamin C) have antioxidant properties that aid in reducing inflammation caused by intense exercise or injury. Minerals like iron and calcium are also critical for optimal recovery.
5. Individual Preferences and Allergies
Lastly, individual preferences and allergies should be taken into account when tailoring recovery nutrition plans. Not everyone may tolerate or enjoy certain foods, so it’s important to find suitable alternatives that still meet their nutritional needs.
Furthermore, those with food allergies or intolerances must avoid triggering ingredients while ensuring they still receive the necessary nutrients for recovery.
VI. Common Mistakes to Avoid in Recovery Nutrition
Proper nutrition is crucial for effective recovery after a workout or intense physical activity. However, many people make common mistakes that can hinder their progress and delay their recovery. To ensure you maximize the benefits of your post-workout nutrition, avoid the following mistakes:
1. Skipping Meals
One of the biggest mistakes people make is skipping meals after exercise. Your body needs nutrients to repair and replenish muscles, so it’s essential to fuel it with a well-balanced meal or snack within an hour of completing your workout.
2. Ignoring Protein Intake
Protein plays a vital role in muscle repair and growth, making it crucial for recovery. Failing to consume enough protein can slow down your body’s ability to rebuild damaged muscle tissues and prolong the recovery process.
3. Overlooking Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are an important source of energy for your body during exercise and help replenish glycogen stores afterward. Neglecting carbohydrates in your post-workout meal can lead to fatigue, reduced performance, and slower recovery.
4. Not Hydrating Adequately
Adequate hydration is essential for optimal muscle function and overall health. Failing to drink enough water before, during, and after exercise can impair performance, delay recovery, and increase the risk of dehydration-related complications.
5. Consuming Excessive Fat
Fat is necessary for overall health but should be consumed in moderation after workouts as it slows down digestion rates compared to protein and carbohydrates consumption alone.
Incorporating healthy fats into your diet is important but consuming excessive amounts immediately after exercising may hinder nutrient absorption and delay the delivery of essential nutrients to your muscles.
6. Relying on Processed Foods
Processed foods often contain high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives. These can negatively impact your recovery by providing empty calories without offering the necessary nutrients your body needs for optimal repair.
7. Neglecting Micronutrients
Vitamins and minerals play a vital role in various bodily processes, including recovery. Ignoring the importance of consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can result in micronutrient deficiencies that may impair your body’s ability to recover efficiently.
8. Not Listening to Your Body
Every individual is unique, so it’s crucial to listen to your body’s signals when it comes to recovery nutrition. Pay attention to how different foods make you feel after workouts and adjust accordingly based on what works best for you.
By avoiding these common mistakes in recovery nutrition, you can optimize your post-workout routine and enhance overall performance while maximizing muscle repair and growth.
VII. Frequently Asked Questions about Recovery Nutrition Principles
1. What is recovery nutrition?
Recovery nutrition refers to the strategic intake of nutrients after physical activity to promote optimal recovery and enhance performance. It involves consuming the right balance of macronutrients and micronutrients to replenish energy stores, repair damaged tissues, and support muscle growth.
2. Why is recovery nutrition important?
Proper recovery nutrition plays a crucial role in restoring glycogen levels, reducing muscle damage, and promoting muscle protein synthesis. It helps speed up the recovery process, minimizes soreness, prevents fatigue, and prepares the body for subsequent training sessions or competitions.
3. What are the key components of a post-workout meal?
A well-rounded post-workout meal should include carbohydrates for replenishing glycogen stores, protein for muscle repair and growth, healthy fats for hormone regulation and joint health, as well as vitamins and minerals to support overall recovery.
4. How soon after exercise should I consume my post-workout meal?
The timing of your post-workout meal is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness. Ideally, you should aim to eat within 30-60 minutes after exercise when your body is most receptive to nutrient uptake. However, if this window is missed due to various circumstances (e.g., busy schedule), consuming a balanced meal within two hours can still provide benefits.
5. Can I rely on supplements alone for recovery nutrition?
No! While supplements can be a convenient option in certain situations or if you have specific dietary restrictions or needs,
it’s important not to solely rely on them as replacements for whole foods.
Whole food sources offer a wide range of essential nutrients that work synergistically to support recovery and overall health.
6. Do I need to adjust my recovery nutrition based on the type of exercise?
Absolutely! The nutritional needs after different types of exercise can vary.
For endurance activities, replenishing glycogen stores with carbohydrates is crucial.
For strength training, consuming enough protein for muscle repair and growth takes priority.
Tailoring your recovery nutrition according to the specific demands of your workouts will optimize your results.
7. Can I have a cheat meal after a workout?
While indulging in occasional treats is fine, it’s important to maintain a balanced approach to post-workout nutrition.
Filling up on unhealthy, high-sugar foods or processed junk may hinder your recovery process and compromise long-term progress.
Opting for nutrient-dense whole foods will provide better support for your body’s recovery needs.
8. How much water should I drink during my recovery period?
Your hydration status significantly affects the effectiveness of your recovery process.
It’s recommended to consume adequate fluids both during and after exercise. The exact amount varies depending on factors like duration and intensity of activity,
environmental conditions, individual sweat rate, etc. Monitoring urine color can serve as an indicator for proper hydration levels.
9. Is it necessary to track macros and calories for post-workout meals?
The importance of tracking macros and calories depends on individual goals and preferences.
If you have specific targets or are trying to manage weight or body composition,
keeping track can help ensure you’re meeting your nutritional requirements consistently over time. However,
for most individuals engaging in regular physical activity without specific goals,
a focus on consuming whole foods in appropriate portion sizes often suffices.
10. Are there any special considerations for vegetarian or vegan athletes regarding recovery nutrition?
Vegetarian and vegan athletes can fulfill their recovery nutrition needs by carefully planning their meals to include a variety of plant-based protein sources, such as legumes, tofu, tempeh,
quinoa, and seitan. Additionally,
paying attention to iron, calcium, vitamin B12,
and omega-3 fatty acid intake is essential for overall health and optimal recovery.

Shelby Cortez is a dynamic and passionate individual with a strong background in the fitness industry. With a Bachelor’s degree in Exercise Science from the prestigious University of California, she has gained extensive knowledge about the human body and its mechanics. Shelby’s dedication to fitness goes beyond her education, as she has spent years honing her skills as a personal trainer and group fitness instructor. Her expertise in workout routines and nutrition has helped countless individuals achieve their fitness goals. Shelby’s commitment to health and wellness is evident in her own lifestyle, as she consistently pushes herself to new limits in the gym. Whether it’s weightlifting, yoga, or HIIT workouts, Shelby Cortez is the go-to expert for all things fitness-related.
