Contents
- I. Introduction to Nutrient Timing for Workouts
- II. Importance of Nutrient Timing in Exercise Performance
- III. Pre-Workout Nutrition Strategies for Optimal Energy Levels
- IV. Post-Workout Nutrition for Muscle Recovery and Growth
- V. Timing Protein Intake for Muscle Building
- VI. Carbohydrate Timing for Fueling Workouts
- VII. The Role of Fats in Nutrient Timing for Workouts
- VIII. Hydration Timing and its Impact on Exercise Performance
- IX. Key Nutrients for Pre and Post-Workout Meals
I. Introduction to Nutrient Timing for Workouts

When it comes to maximizing the benefits of your workouts, it’s not just about what exercises you do or how hard you push yourself. Another crucial factor that often gets overlooked is nutrient timing – the strategic consumption of macronutrients before, during, and after exercise. By properly fueling your body at specific times, you can enhance performance, optimize recovery, and achieve better results from your workouts.
Fueling Pre-Workout:
One important aspect of nutrient timing is ensuring that you have adequate fuel before starting your workout. Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for high-intensity activities, so consuming a balanced meal or snack containing carbs and some protein around 1-3 hours before exercising can provide the necessary energy boost.
Eating During Exercise:
For longer workouts lasting more than 60 minutes or intense endurance training sessions, refueling during exercise becomes vital. Consuming easily digestible carbohydrates like sports drinks or energy gels can help maintain blood sugar levels and delay fatigue by providing a quick source of energy.
The Post-Workout Recovery Window:
After completing a workout session, there’s a critical period known as the “post-workout recovery window” where your body is primed to replenish glycogen stores and repair damaged muscle tissues. To make the most out of this window, consuming both carbohydrates and protein within 30 minutes to an hour after exercise is recommended.
The Role of Protein:
In addition to carbohydrates’ importance in providing energy during workouts, protein plays a crucial role in repairing and building muscles. Including some lean sources of protein in post-workout meals helps kickstart muscle recovery processes by supplying essential amino acids needed for tissue repair and growth.
Hydration Matters:
Proper hydration is a key element of nutrient timing. Dehydration can negatively impact performance, so it’s essential to drink fluids before, during, and after exercise. Aim for sipping water or electrolyte-rich beverages regularly throughout your workout to maintain optimal hydration levels.
II. Importance of Nutrient Timing in Exercise Performance

Nutrient timing refers to the strategic consumption of specific nutrients before, during, and after exercise to optimize performance and enhance recovery. This practice has gained significant attention among athletes and fitness enthusiasts due to its potential benefits in maximizing training adaptations.
The Pre-Workout Window: Fueling Your Body for Success
One crucial aspect of nutrient timing is consuming the right nutrients before your workout. By providing your body with a combination of carbohydrates and protein, you can fuel your muscles adequately and optimize energy levels during exercise. Carbohydrates serve as the primary source of energy for high-intensity workouts, while protein helps support muscle growth and repair.
Consider incorporating easily digestible carbohydrates like fruits or whole grains into your pre-workout meal or snack. Pair it with a lean source of protein such as chicken breast or Greek yogurt to promote muscle recovery and prevent muscle breakdown during exercise.
Intra-Workout Nutrition: Sustaining Energy Levels
The importance of nutrient timing extends beyond pre-workout nutrition; it also encompasses what you consume during exercise. For prolonged workouts lasting longer than 60 minutes, consuming a carbohydrate-rich beverage can help sustain energy levels by providing a readily available fuel source.
A sports drink containing electrolytes can be beneficial for replenishing fluids lost through sweat while enhancing hydration status during intense physical activity. Additionally, including branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) can further aid in reducing muscle fatigue and promoting endurance.
Post-Workout Recovery: Repairing Muscles & Replenishing Nutrients
The post-workout period is crucial for initiating the recovery process by repairing damaged muscles and replenishing depleted glycogen stores. Consuming a combination of carbohydrates and protein within 30 minutes to an hour after exercise can enhance this recovery process.
Carbohydrates help replenish glycogen stores, while protein provides the necessary amino acids for muscle repair and growth. Optimal choices include a protein shake with added carbohydrates or a balanced meal consisting of lean protein, whole grains, and vegetables.
Optimizing Nutrient Timing: Personalization is Key
It’s important to note that nutrient timing may vary depending on individual goals, exercise intensity, and duration. Experimenting with different strategies and paying attention to your body’s response can help you find the ideal approach that optimizes your exercise performance.
III. Pre-Workout Nutrition Strategies for Optimal Energy Levels
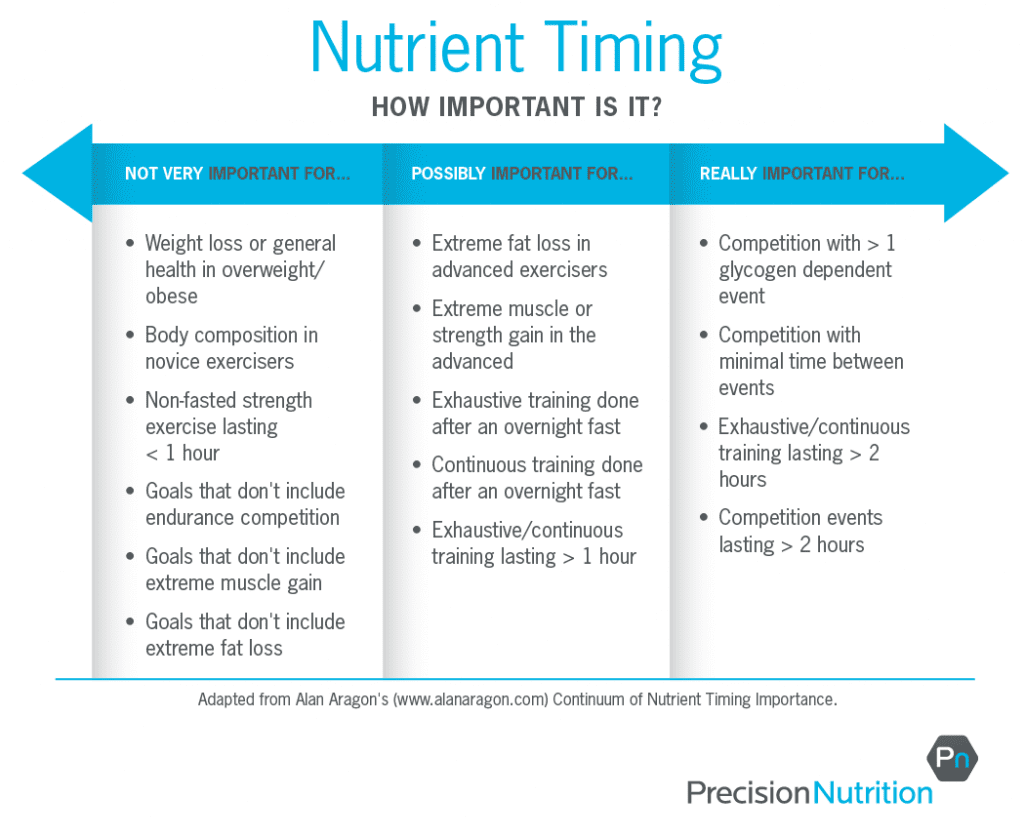
When it comes to maximizing your performance during workouts, paying attention to your pre-workout nutrition is crucial. The food you consume before hitting the gym can significantly impact your energy levels, endurance, and overall performance. Here are some effective strategies to optimize your pre-workout nutrition:
1. Fuel Up with Complex Carbohydrates
Prioritize consuming complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, sweet potatoes, and brown rice before your workout. These slow-digesting carbs provide a steady release of energy during exercise and help sustain high-intensity efforts.
2. Include Lean Protein Sources
Incorporate lean protein sources like chicken breast, fish, tofu, or Greek yogurt into your pre-workout meal or snack. Protein plays a vital role in muscle repair and recovery while also providing a sustained source of energy throughout your workout.
3. Hydrate Properly
Adequate hydration is essential for optimal performance in any physical activity. Make sure to drink enough water before exercising to prevent dehydration and maintain proper electrolyte balance in the body.
4. Time Your Meals Wisely
Avoid eating large meals right before working out as they may cause discomfort during exercise due to digestion demands on the body. Aim to have a balanced meal containing carbs and protein about 1-2 hours prior to training sessions.
5. Consider Pre-Workout Supplements
If you need an extra boost of energy and focus during workouts, consider incorporating pre-workout supplements into your routine after consulting with a healthcare professional or fitness expert.
These strategies will help ensure that you have sufficient fuel for intense workouts while minimizing the risk of digestive discomfort. Remember, experimenting with different approaches and finding what works best for your body is key to optimizing your pre-workout nutrition routine.
IV. Post-Workout Nutrition for Muscle Recovery and Growth

After a grueling workout session, it’s crucial to replenish your body with the right nutrients to support muscle recovery and growth. The post-workout period is a critical time when your muscles are primed to absorb nutrients, making it essential to provide them with the necessary fuel they need.
The Importance of Protein Intake
Protein plays a significant role in repairing damaged muscle tissues and promoting muscle growth. Consuming an adequate amount of protein after your workout helps kickstart the recovery process. Aim for 20-30 grams of high-quality protein from sources like lean meats, fish, eggs, or plant-based options such as tofu or legumes.
Incorporating Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are essential post-workout as they replenish glycogen stores that get depleted during intense exercise. Opt for complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables that provide sustained energy release. Consuming carbohydrates alongside protein promotes better absorption of amino acids into the muscles.
The Role of Healthy Fats
Incorporating healthy fats into your post-workout meal aids in reducing inflammation and supporting overall health. Include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids such as salmon, avocados, or nuts to promote faster recovery and reduce muscle soreness.
Hydration Matters
Don’t forget about hydration! Properly rehydrating after exercise is vital for optimal recovery. Water should be your go-to choice; however, if you’ve engaged in prolonged intense workouts or sweat excessively during training sessions, consider adding electrolytes through sports drinks or natural coconut water.
Sleep: The Ultimate Recovery Aid
No discussion of post-workout recovery would be complete without mentioning the importance of sleep. During sleep, your body repairs and rebuilds damaged muscle tissues. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to maximize the benefits of your workout and support overall muscle growth.
V. Timing Protein Intake for Muscle Building
When it comes to building muscle, timing your protein intake is crucial. The right amount of protein at the right time can maximize muscle growth and recovery. Here are some key points to consider:
The Anabolic Window Myth
Contrary to popular belief, there is no specific “anabolic window” immediately after a workout where you must consume protein or risk losing gains. Research has shown that the body’s ability to utilize protein for muscle synthesis extends beyond this narrow timeframe.
Pre-Workout Protein
To optimize muscle building, it’s recommended to consume a small amount of high-quality protein before your workout session. This can provide amino acids for fuel during exercise and help kickstart the recovery process.
Intra-Workout Protein
Sipping on a protein shake during your workout may not be necessary unless you have an exceptionally long training session or engage in endurance activities like marathon running or cycling. In most cases, focus on staying hydrated with water or electrolyte drinks instead.
Post-Workout Protein
The post-workout period remains an important time to replenish your body with nutrients, including protein. Consuming around 20-30 grams of high-quality protein within two hours after intense exercise can enhance muscle repair and growth.
Distribution throughout the Day
While immediate post-workout nutrition is important, spreading out your total daily protein intake across multiple meals has been found to be equally beneficial for maximizing muscle building potential. Aim for consuming adequate amounts of quality proteins throughout the day rather than relying solely on one large serving.
In conclusion, timing your protein intake strategically plays a role in optimizing muscle building outcomes. While there is no need to obsessively watch the clock for a specific anabolic window, ensuring regular protein intake throughout the day and around your workouts can support muscle recovery and growth. Remember that individual needs may vary, so it’s always best to consult with a qualified nutritionist or health professional to tailor your protein timing strategies to your specific goals and requirements.
VI. Carbohydrate Timing for Fueling Workouts
When it comes to optimizing your workouts and maximizing performance, carbohydrate timing plays a crucial role. Understanding when and how to fuel your body with carbohydrates can greatly impact your energy levels, endurance, and overall workout effectiveness.
The Pre-Workout Carbohydrate Boost
Prior to hitting the gym or engaging in any physical activity, consuming carbohydrates is essential for providing your muscles with the necessary fuel they need. By consuming a meal or snack rich in complex carbohydrates about 1-3 hours before your workout, you are giving your body enough time to properly digest and absorb these nutrients.
This pre-workout carbohydrate boost will help replenish glycogen stores in the muscles, which serve as an energy source during exercise. Additionally, it ensures that there is enough blood glucose available during intense workouts or prolonged sessions.
Intra-Workout Carbohydrates for Sustained Energy
If you’re engaged in long-duration workouts lasting more than 60 minutes or high-intensity exercises such as interval training or weightlifting sessions, incorporating intra-workout carbohydrates can provide sustained energy levels throughout the session.
Consuming easily digestible sources of carbohydrates like sports drinks, gels, or fruit can help maintain blood glucose levels and delay fatigue during extended periods of exertion. These quick-digesting carbs rapidly enter the bloodstream and provide an immediate source of fuel for working muscles.
Post-Workout Carbs for Recovery
The post-workout period is crucial for replenishing glycogen stores depleted during exercise and promoting muscle recovery. Consuming a combination of fast-digesting carbs along with protein within 30 minutes after completing your workout helps kickstart this recovery process.
Carbohydrates with a high glycemic index, such as white rice or potatoes, are recommended during this time as they rapidly spike insulin levels and drive nutrients into the muscles. This aids in replenishing glycogen stores and facilitating muscle repair.
Individual Variations in Carbohydrate Timing
While general guidelines exist for carbohydrate timing, it’s important to note that individual variations may occur. Factors such as body composition, exercise intensity and duration, training goals, and personal preferences can influence the optimal timing and quantity of carbohydrates consumed before, during, and after workouts.
Experimentation is key to finding what works best for you. Pay attention to how your body responds to different carbohydrate timings and adjust accordingly. Consulting with a registered dietitian or sports nutritionist can also provide personalized guidance based on your specific needs.
Carbohydrate timing is an essential component of fueling workouts effectively. By strategically consuming carbohydrates before, during, and after training sessions based on individual needs and goals, you can optimize performance levels while supporting muscle recovery. Experimentation combined with expert advice will help you find the perfect balance that allows you to reach your fitness potential.
VII. The Role of Fats in Nutrient Timing for Workouts
When it comes to optimizing your workout performance and recovery, nutrient timing is crucial. While proteins and carbohydrates often steal the spotlight, fats play a significant role in this process as well. Let’s explore how fats contribute to nutrient timing for workouts.
Fuel for Endurance
Fats are an excellent source of energy that can fuel your workouts, especially during endurance activities. Unlike carbohydrates, which provide quick energy but can be depleted rapidly, fats offer a sustained release of energy throughout prolonged exercise sessions. By incorporating healthy fats into your pre-workout meals or snacks, you can ensure a steady supply of fuel to power through intense training sessions.
Enhanced Nutrient Absorption
Fat plays a vital role in the absorption and transportation of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) and other nutrients essential for optimal health and exercise performance. Including moderate amounts of healthy fats in your post-workout meal helps facilitate the absorption of these crucial nutrients from other foods you consume alongside them.
Inflammation Reduction
Intense workouts can lead to inflammation within the body due to oxidative stress on muscles and tissues. Healthy dietary fats possess anti-inflammatory properties that aid in reducing inflammation caused by exercise-induced muscle damage. By including sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, or fatty fish such as salmon in your post-workout meal or snack options can help mitigate this inflammation and promote faster recovery.
Hormone Regulation
Fats play a pivotal role in hormone production and regulation within our bodies. Hormones such as testosterone are essential for muscle growth and repair after workouts. Including healthy sources of fat like olive oil or coconut oil aids hormonal balance and ensures proper muscle recovery. Additionally, fats also help regulate insulin levels, promoting stable blood sugar levels during and after exercise.
Mental Focus and Satiety
Consuming adequate amounts of healthy fats can contribute to improved mental focus during workouts. Fats provide a longer-lasting feeling of satiety compared to carbohydrates alone, which can help you stay focused and energized throughout your training session. Including sources like nuts, seeds, or nut butter in your pre-workout meals or snacks can enhance cognitive function while providing sustained energy.
In conclusion, while proteins and carbohydrates are often the main focus when it comes to nutrient timing for workouts, fats should not be overlooked. Incorporating healthy fats into your pre- and post-workout meals can provide sustained energy, aid nutrient absorption, reduce inflammation, regulate hormones, improve mental focus, and promote satiety. Remember to choose sources of healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, seeds or fatty fish to reap these benefits for optimal workout performance and recovery.
VIII. Hydration Timing and its Impact on Exercise Performance
Hydration plays a crucial role in optimizing exercise performance, as even mild dehydration can have detrimental effects on an individual’s physical capabilities. It is important to understand the timing of hydration during workouts to ensure proper fluid balance and prevent any negative impacts.
The Pre-Workout Hydration Strategy
Prior to embarking on your workout session, it is essential to hydrate adequately. Proper pre-workout hydration ensures that your body starts the exercise with optimal fluid levels, enhancing endurance and overall performance. Aim to consume approximately 17-20 ounces (500-600 ml) of water or a sports drink two hours before exercising.
However, be mindful not to overhydrate immediately before your workout, as this can lead to discomfort and even hinder performance. It is best practice not to consume large amounts of fluids within 30 minutes of starting your exercise routine.
Hydration During Exercise
Maintaining hydration throughout your workout session is vital for sustaining energy levels and preventing dehydration-related issues such as muscle cramps or fatigue. The American Council on Exercise suggests consuming 7-10 ounces (200-300 ml) of fluid every 10-20 minutes during physical activity.
If you are engaging in prolonged or intense exercise lasting more than one hour, incorporating a sports drink containing electrolytes can be beneficial. Electrolytes help replenish the minerals lost through sweat and aid in maintaining proper muscle function.
Post-Workout Rehydration
Your post-workout rehydration strategy is equally important as pre-and intra-workout hydration for optimal recovery and overall well-being. After completing your exercise routine, aim to consume at least 16 ounces (475 ml) of water or a sports drink within 30 minutes.
Replenishing fluids post-workout helps restore hydration levels, supports muscle recovery, and aids in flushing out metabolic waste products. Including some sodium in your post-exercise beverage can be beneficial as it aids in fluid retention and enhances rehydration.
Individual Factors to Consider
It is important to note that individual factors such as body weight, sweat rate, exercise intensity, and environment can impact your hydration needs during workouts. Pay attention to your body’s signals and adjust your fluid intake accordingly.
If you are unsure about your specific hydration requirements or have any underlying health conditions, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian who specializes in sports nutrition.
Overall, understanding the timing of hydration during exercise is crucial for optimizing performance. By following appropriate pre-, intra-, and post-workout hydration strategies tailored to individual needs, you can ensure you stay properly hydrated throughout your training sessions. Remember to listen to your body’s cues and make adjustments as necessary for optimal results.
IX. Key Nutrients for Pre and Post-Workout Meals
When it comes to maximizing your workout performance and recovery, paying attention to what you eat before and after your training sessions is crucial. Your body needs the right combination of nutrients to fuel your workouts, promote muscle growth, and enhance recovery. Here are some key nutrients that you should include in your pre and post-workout meals:
1. Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for our bodies during physical activity. Consuming carbohydrates before a workout provides the necessary fuel to perform at your best. Opt for complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes as they provide a steady release of energy.
2. Protein
Protein plays a vital role in repairing damaged muscle tissues and promoting muscle growth after exercise. Including high-quality protein sources such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products or plant-based options like beans or tofu in your post-workout meal helps support muscle recovery.
3. Healthy Fats
Incorporating healthy fats into your pre-workout meal can help provide sustained energy throughout your training session. Avocadoes, nuts/seeds, olive oil or fatty fish like salmon are excellent sources of healthy fats that assist with hormone production while also reducing inflammation.
4. Hydration
Maintaining proper hydration levels is essential both before and after exercise to optimize performance and aid in recovery by replacing fluids lost through sweat during physical activity.
5. Electrolytes
To maintain fluid balance within the body during intense workouts or hot conditions when sweating is increased; electrolytes such as sodium,potassium,and magnesium must be replenished. Including foods like bananas, coconut water, and sports drinks can help restore electrolyte balance.
By prioritizing these key nutrients in your pre and post-workout meals, you are setting yourself up for success on your fitness journey. Remember to listen to your body’s needs and adjust your nutrient intake accordingly based on the intensity and duration of your workouts.

Shelby Cortez is a dynamic and passionate individual with a strong background in the fitness industry. With a Bachelor’s degree in Exercise Science from the prestigious University of California, she has gained extensive knowledge about the human body and its mechanics. Shelby’s dedication to fitness goes beyond her education, as she has spent years honing her skills as a personal trainer and group fitness instructor. Her expertise in workout routines and nutrition has helped countless individuals achieve their fitness goals. Shelby’s commitment to health and wellness is evident in her own lifestyle, as she consistently pushes herself to new limits in the gym. Whether it’s weightlifting, yoga, or HIIT workouts, Shelby Cortez is the go-to expert for all things fitness-related.
